My name is Alan Conder. I work at GMTO and this is my first trip to Magellan; in fact, this is my first trip to any observatory.
I came to Magellan to participate with the team from SAO to field the GMT prototype phasing camera. In addition, I arrived a week early to test a new laser scintillometer at cerro Las Campanas. We plan to use this device to measure the Cn2 of the surface layer at the GMT site.
I was asked to write a post to this blog describing my experiences as a neophyte at Las Campanas. So OK. I’ll do it. My story will be brief and is intended to poke fun of my niave expectations about coming to LCO. And as I make fun of myself, I want to be clear that my experiences have been fantastic. And that everything I was told was absolutely true.
To start, I was told to expect the nights at the telescope to be cold and to come prepared. So I went to REI and bought warm clothing that would protect me on Mt. Everest.
This is me, trying on the warm clothing I had just bought for this experience.
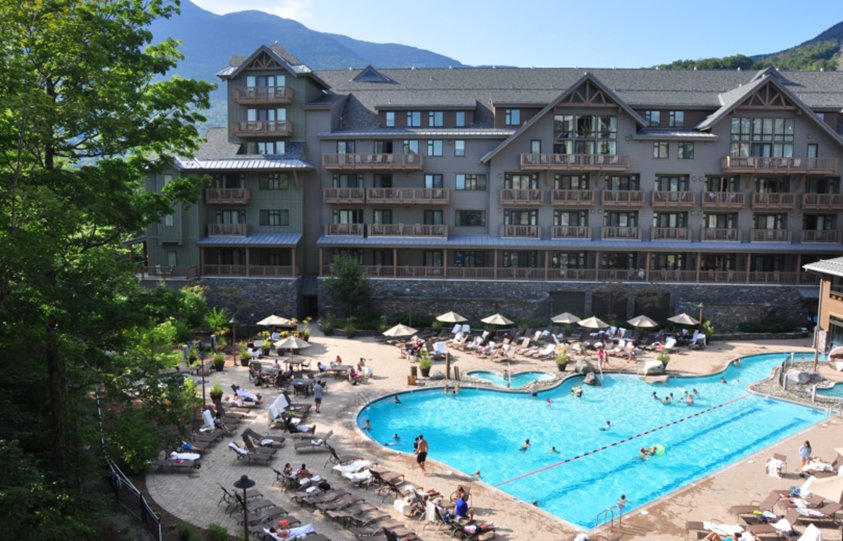
I was told the LCO lodge was in the Andes foothills, with beautiful views, and that in fact there was a hot tub. So I imagined something like the Stowe Mountain Lodge in Vermont. OK, may be a little more quiant.
It is true, there “was” a hot tub. I was a little concerned that there would actually be a hot tub.
I was told that the skies were almost never cloudy.

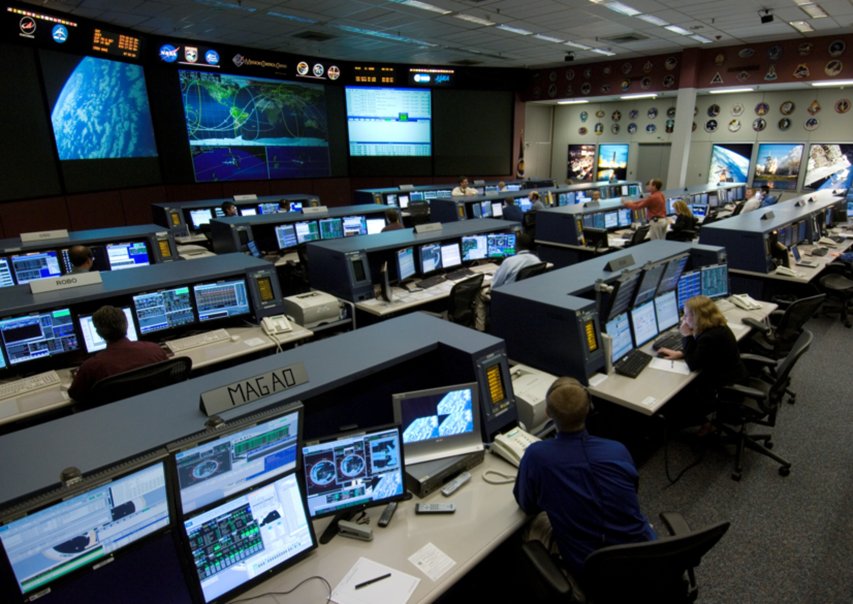
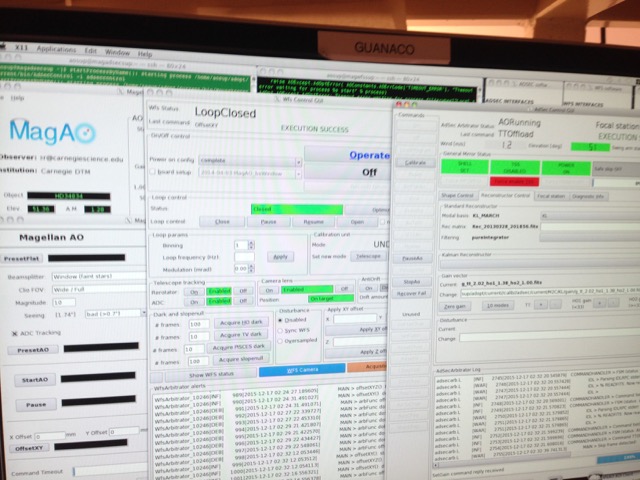
I was told that MagAO had its own console in the control room. This is what I imagined.
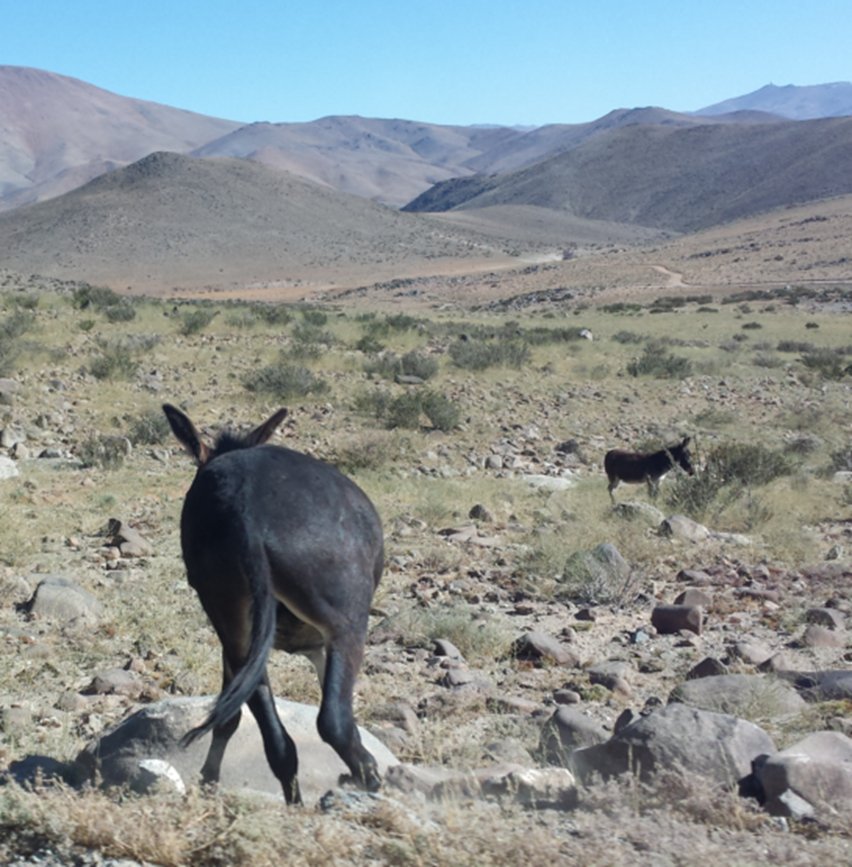
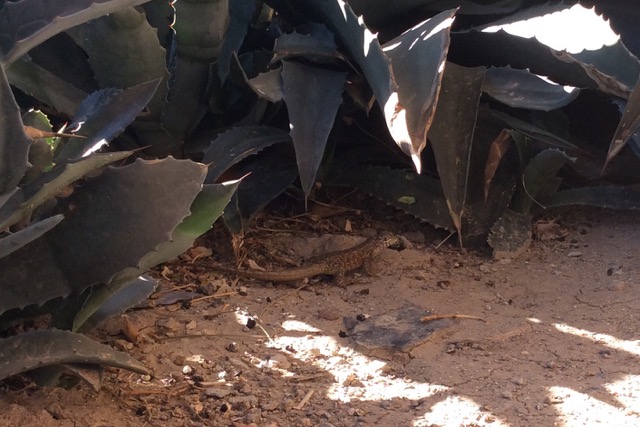
I was told that the wildlife was very different. I tried to photograph wildlife, but it was difficult. However, I was eventually able to photograph an ass.
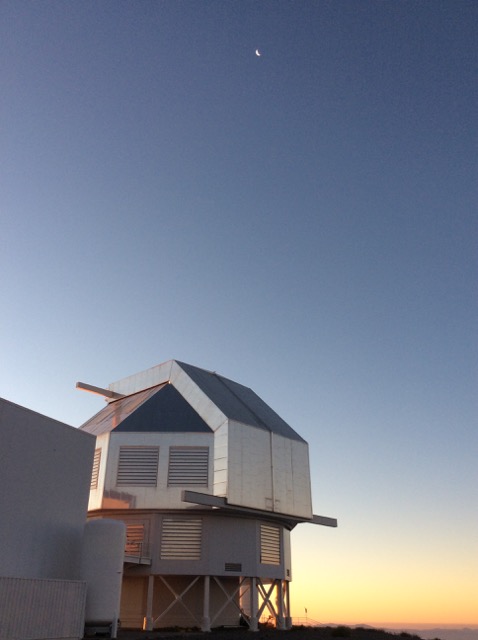
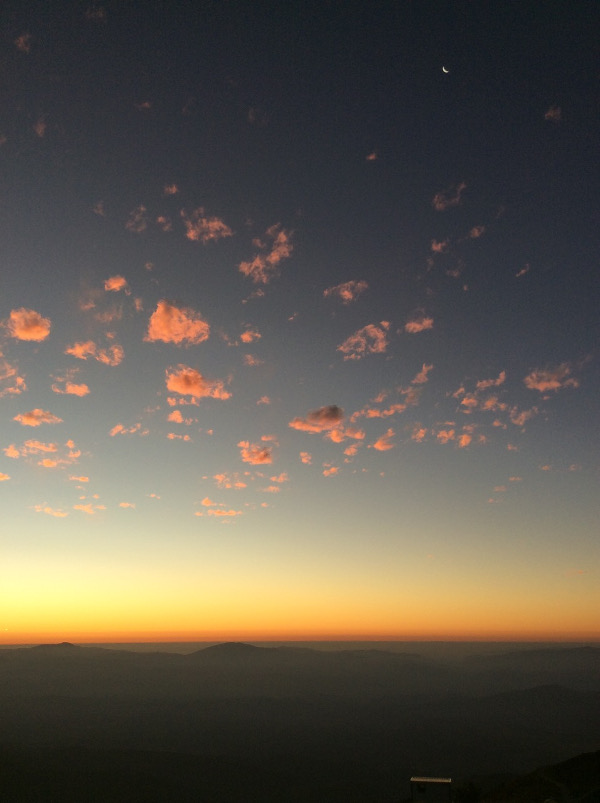
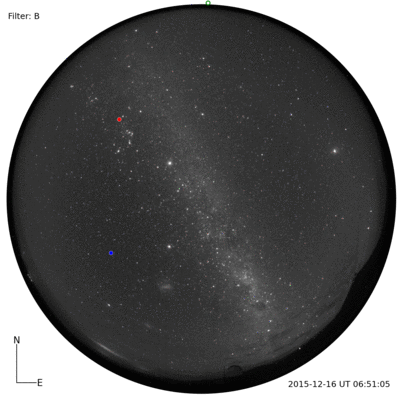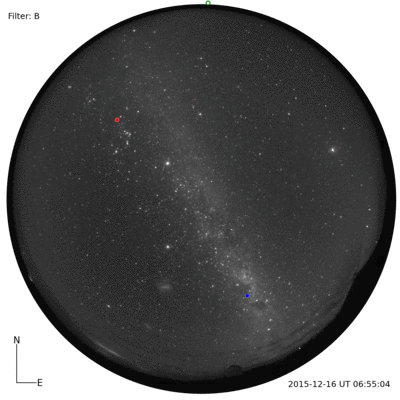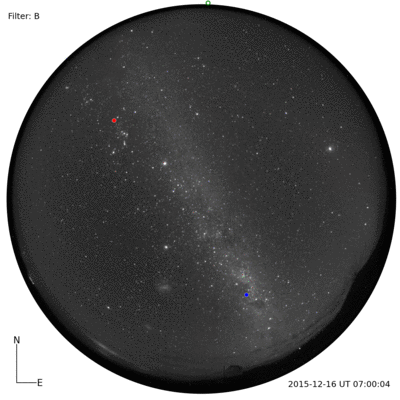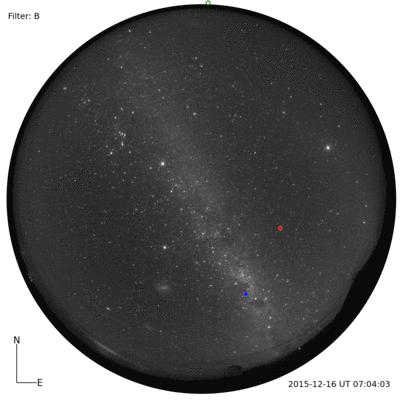
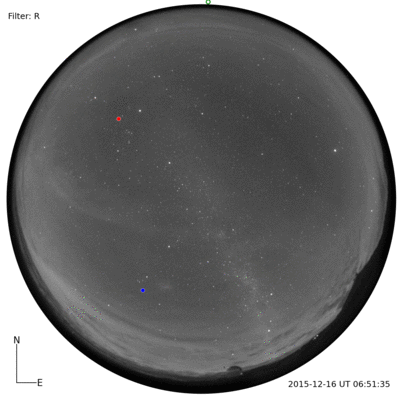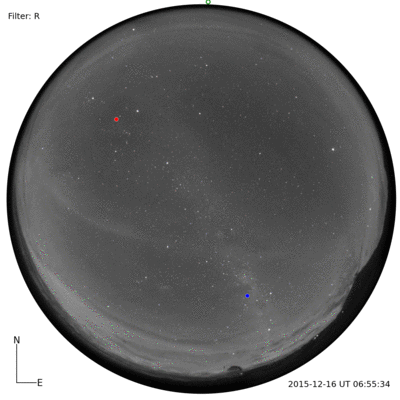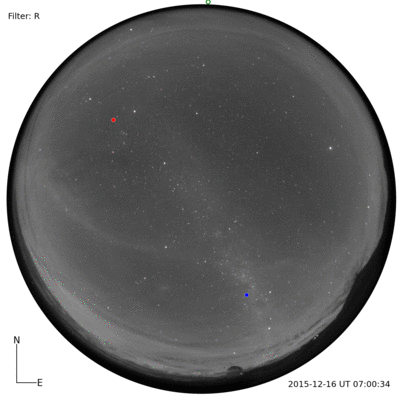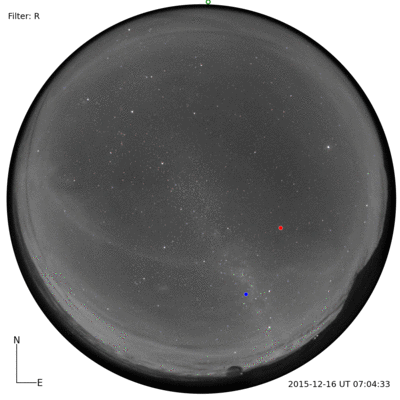
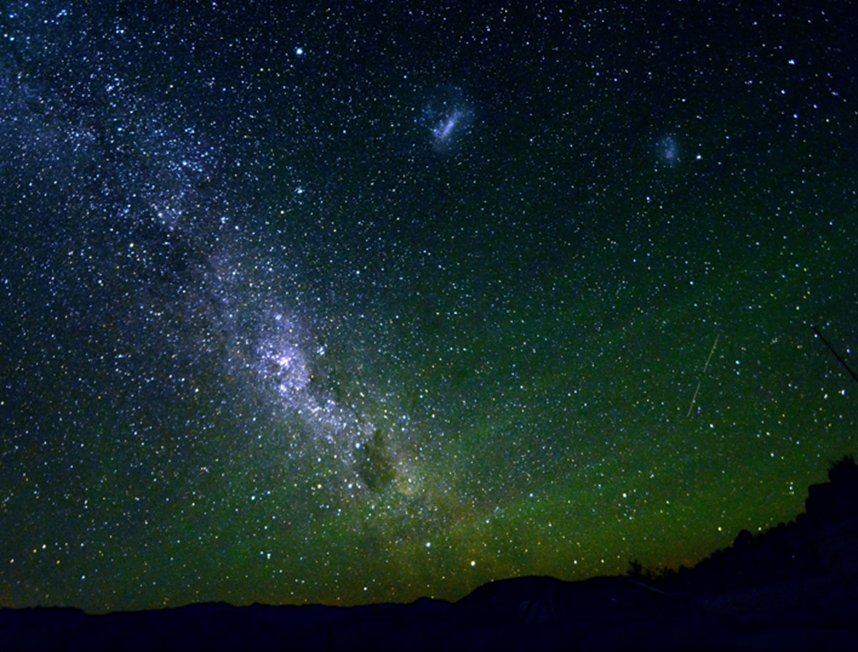
I was told that the night skies are spectacular. And, the night skies are spectacular. I couldn’t even imagine until I saw for myself. A couple of photographs with a commercial Nikon camera.


And of course we did work. Here are some photographs of my colleagues at work. Notice that you don’t see me in any of the photographs.
Starting with the work at cerro Las Campanas.
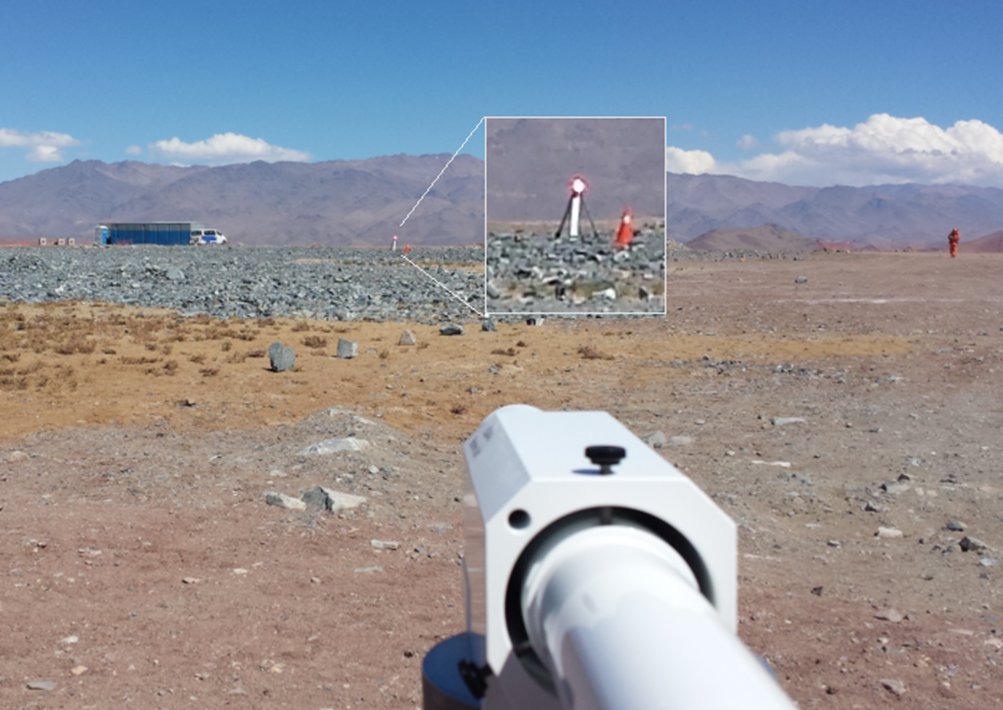
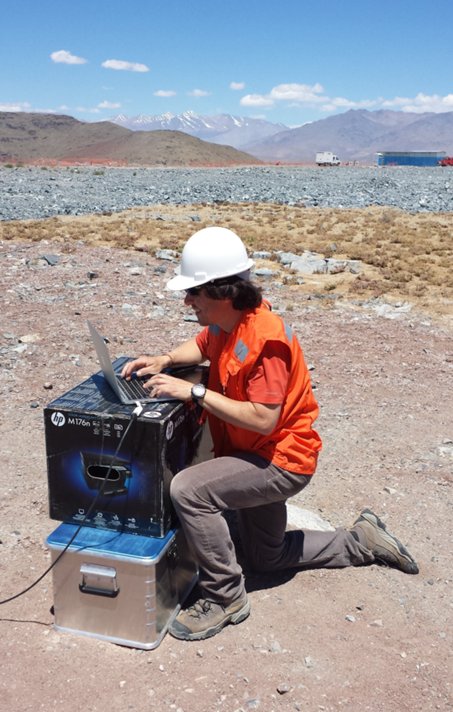


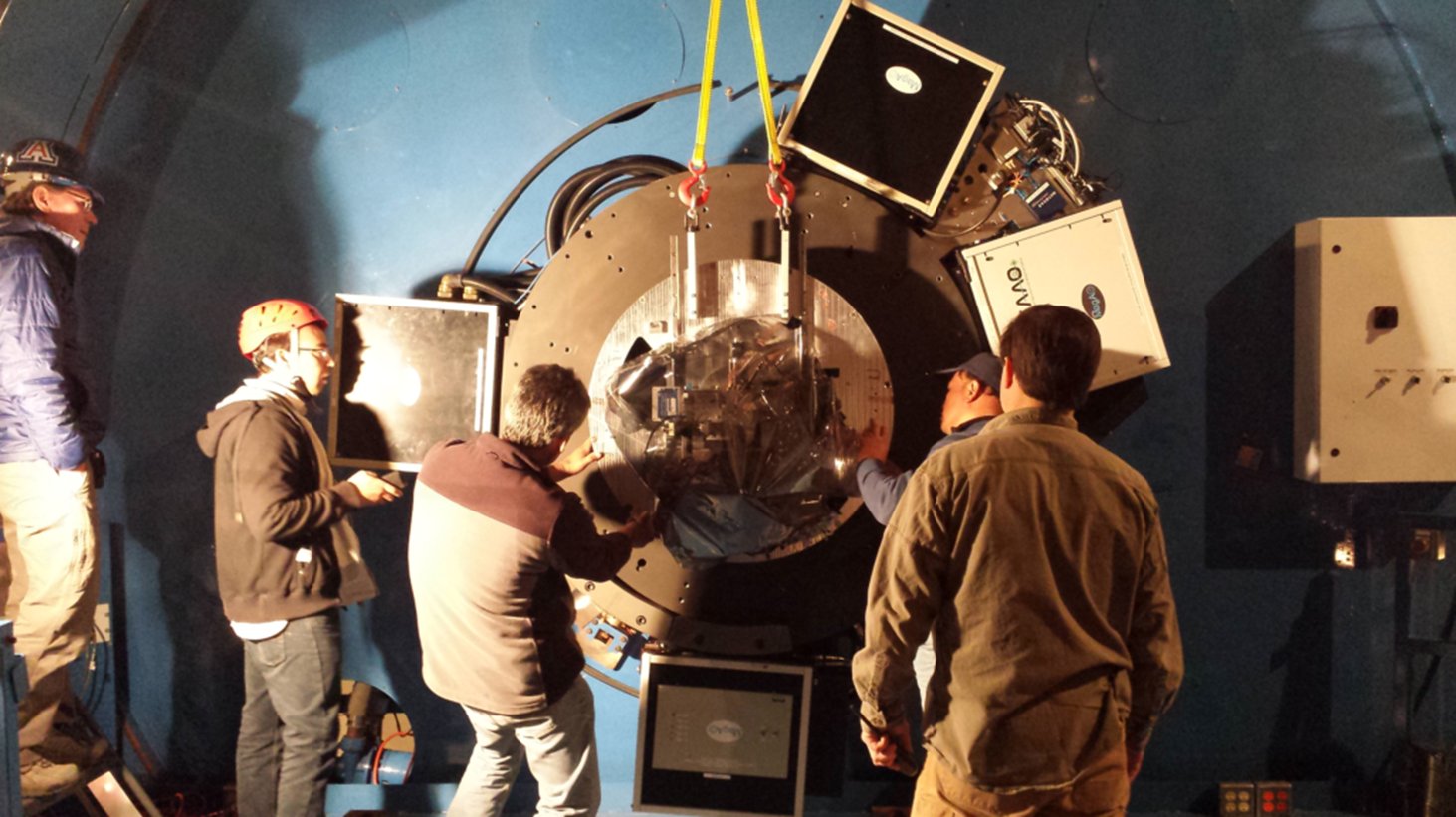
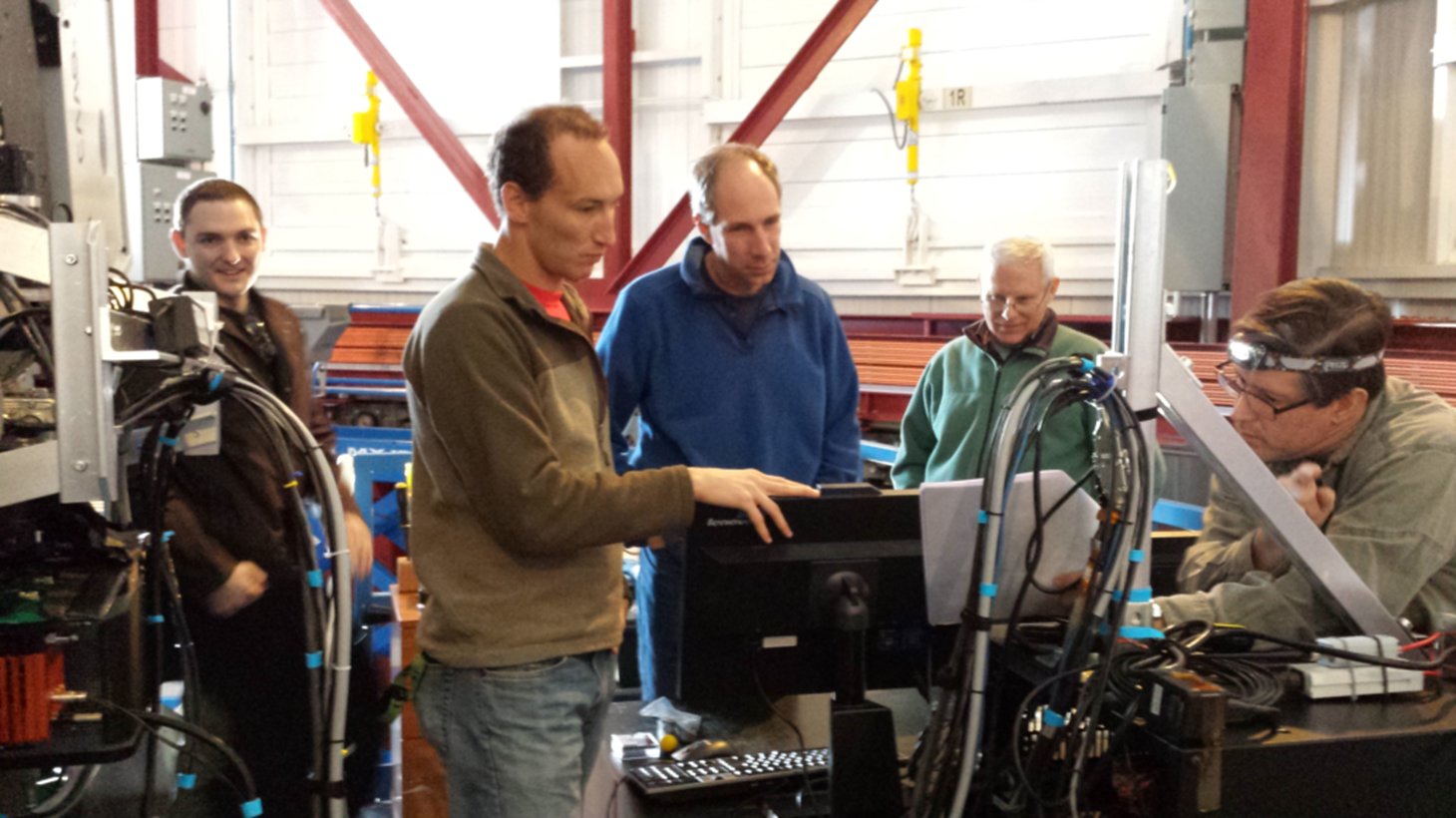
And the work to field the GMT prototype phasing camera.


This is me after about 1 ½ weeks at LCO. A little more facial hair than when I arrived, but no worse for wear and with a soul that has been rejuvenated by the experience.
And finally, the song. Yesterdays blog featured the First Lady of Song, Ella Fitzgerald. And I thought of the tenor sax legend and the Prez of Jazz, Lester Young. The song, “Stardust.”