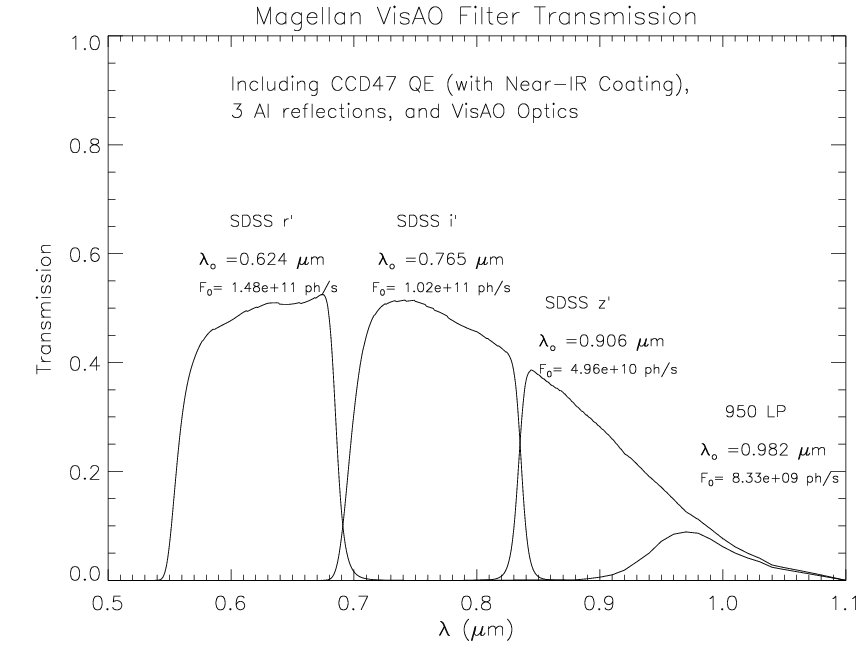
I have updated our VisAO filter curves to now include the effects of 3 reflections from Aluminum mirrors (important because Al has a feature at 0.8 microns), the Clio dichroic, the AR coated surfaces of the VisAO Optics, and the protected silver gimbal mirror in the VisAO camera. Most of these are small losses, but 3 Al reflections are fairly costly at only ~90% reflectance each. I have also convolved the resultant curves with the HST/STIS Vega spectrum to give the approximate photon flux in each filter from a 0 magnitude star. The only major thing not included in these calculations is the reflectance of the beam splitter, since it will vary depending on AO system setup.