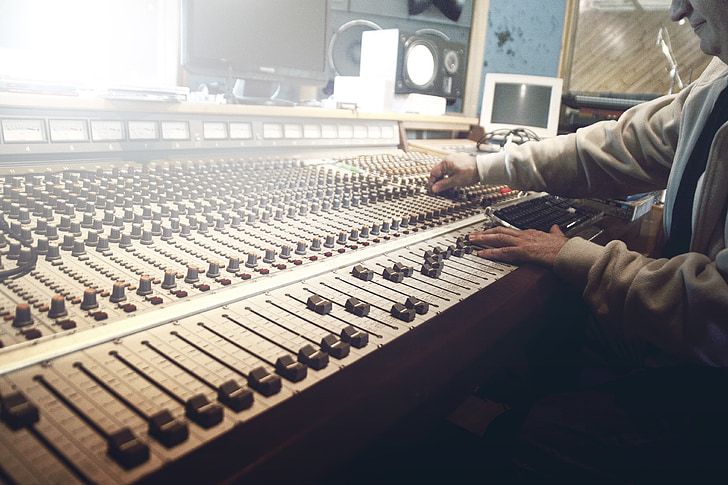
MAPS is The MMT Adaptive optics exoPlanet characterization System, an upgraded adaptive secondary AO system for MMT. For the next week or so, it is installed on the telescope and the team has important engineering and science to do. To this effort, the XWCL has contributed one CACAO expert on the ground (Eden McEwen) and two remotely (Jared Males & Olivier Guyon). We tried to contribute two on the ground, but the departure of Avalon from Tucson means there was a vacancy in the dorms.
I’ve always wanted to see the MMT, ever since the daily high in Tucson cracked 95ºF (if not longer!). I expressed this wish to Manny, and someone vouched for me as “useful”, and thus did I secure Avalon’s spot for myself.
Now, on the MagAO-X team, our fearless leader likes to surprise and alarm us by turning up in unexpected places—to the point where we have a calendar tracking his movements so we know what timezone he’s operating under. Most recently, we learned he was in Tokyo thanks to Hello Kitty.
I thought it was time to return the favor, by heading up Mount Hopkins without a peep to Jared. We had it all worked out: Eden was going to write blog posts with me lurking in the background of her pictures, and we were going to wait and see if Jared noticed… but the cat’s out of the bag already.
And Eden’s asleep.
So I’m writing the blog post.
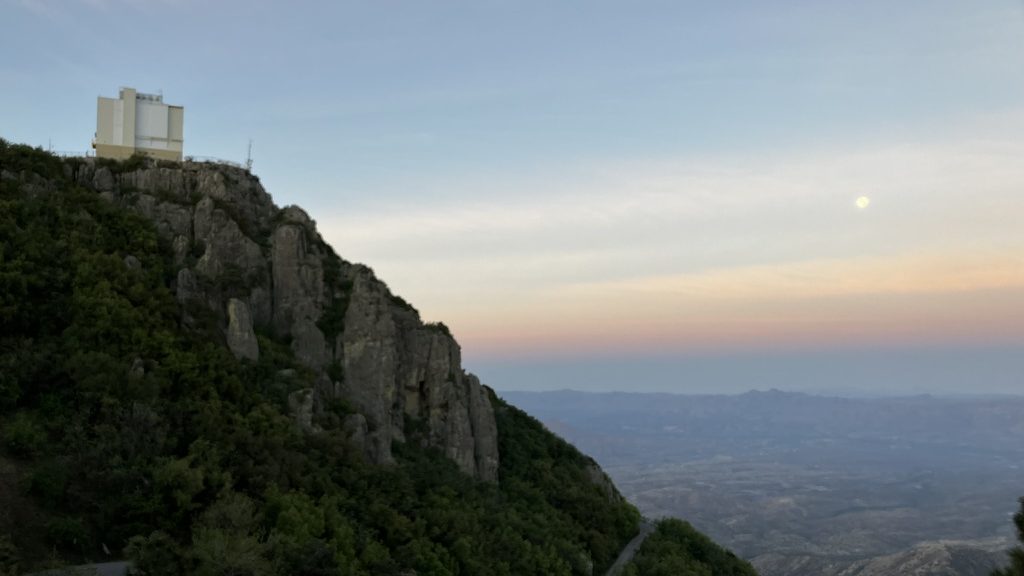
MMT, formerly the Multiple Mirror Telescope (currently the Mmt Mmt Telescope), is a 6.5-meter telescope in Southern Arizona at the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory. It’s part of Steward Observatory, and University of Arizona. Also the Smithsonian. Also Harvard. Everyone wants a piece of the F.L.W.O., and who can blame them? It’s gorgeous country out here.
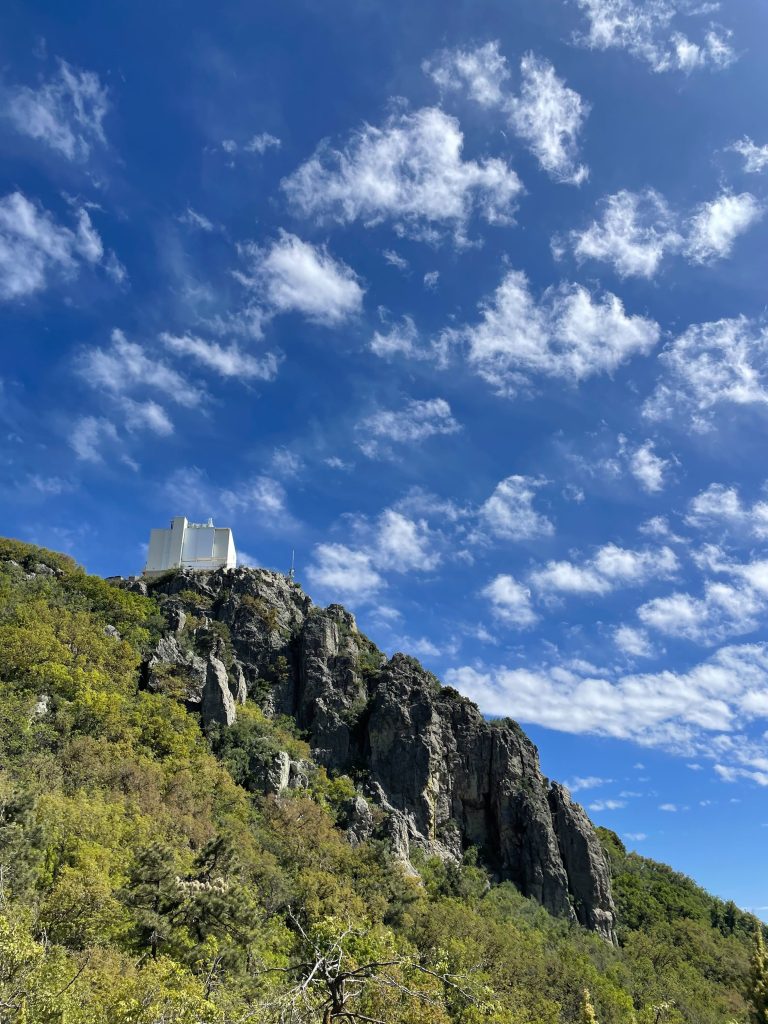


The night shift left Tucson around 1 P.M. with all the food for their 1–6 days of meals in tow (depending on length of stay). With a mere hour-and-a-half drive separating their lab in Tucson from their telescope, the MAPS team has MagAO-X thoroughly beat for convenience.
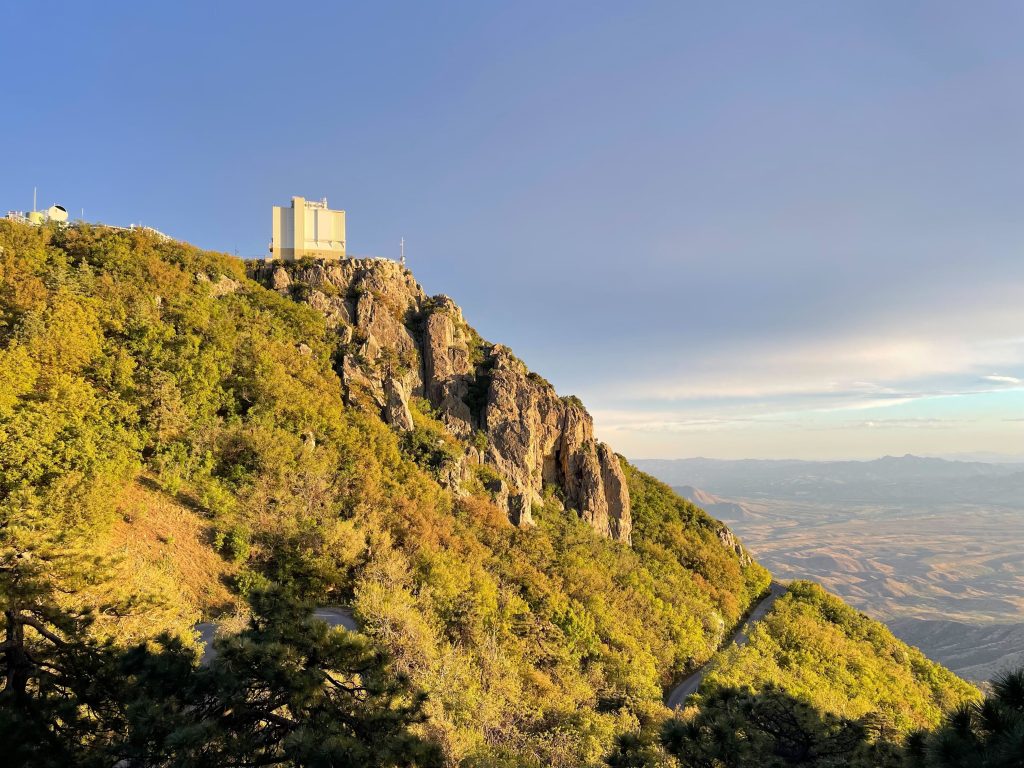
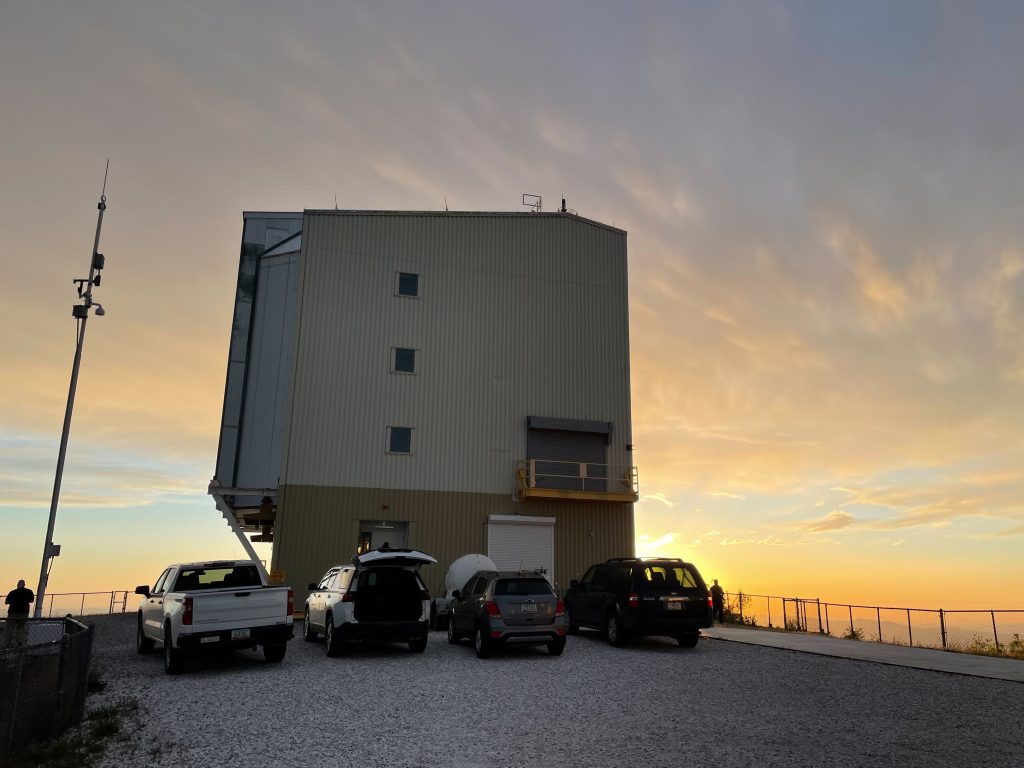
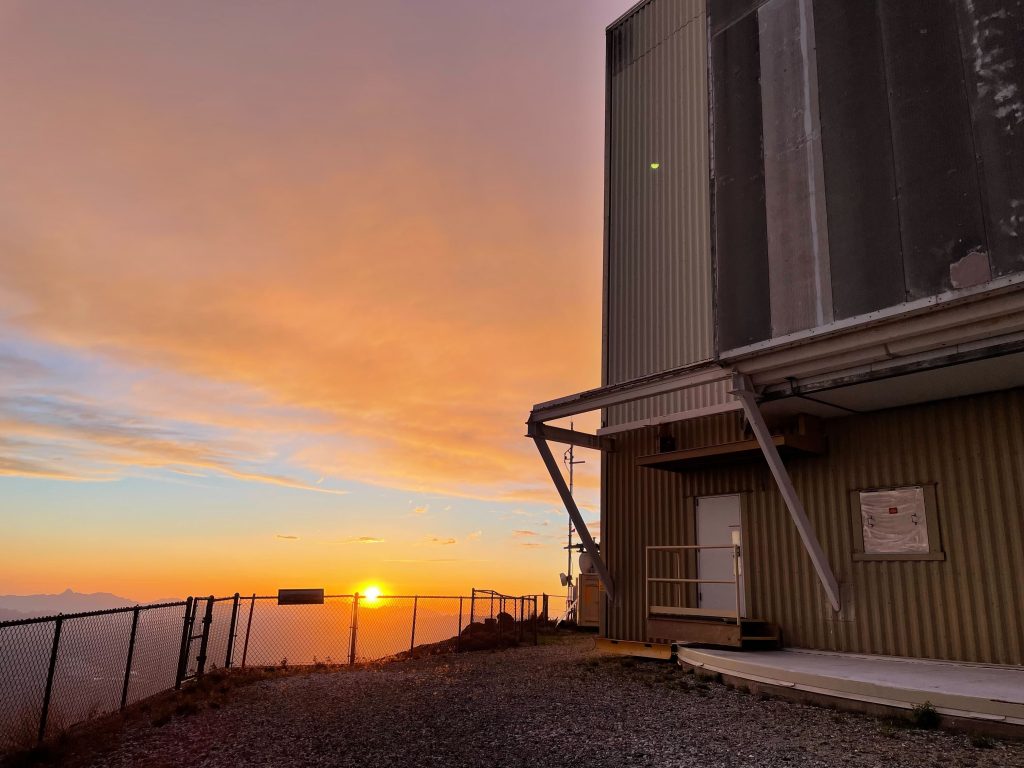
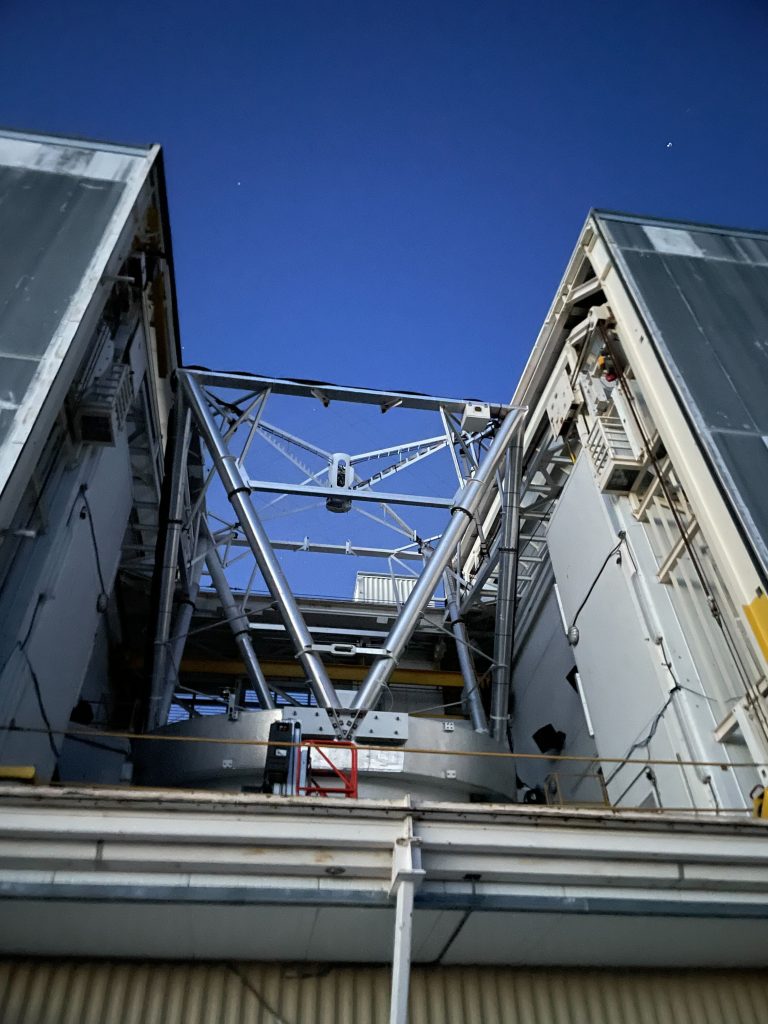
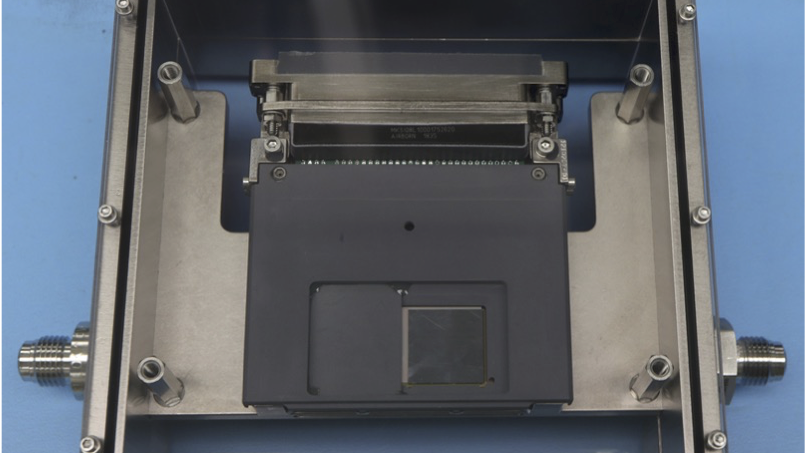
The delicate optical bits were all in place well before sunset, thanks to efforts of the day team, allowing me to take this glamour shot when we opened up the dome.
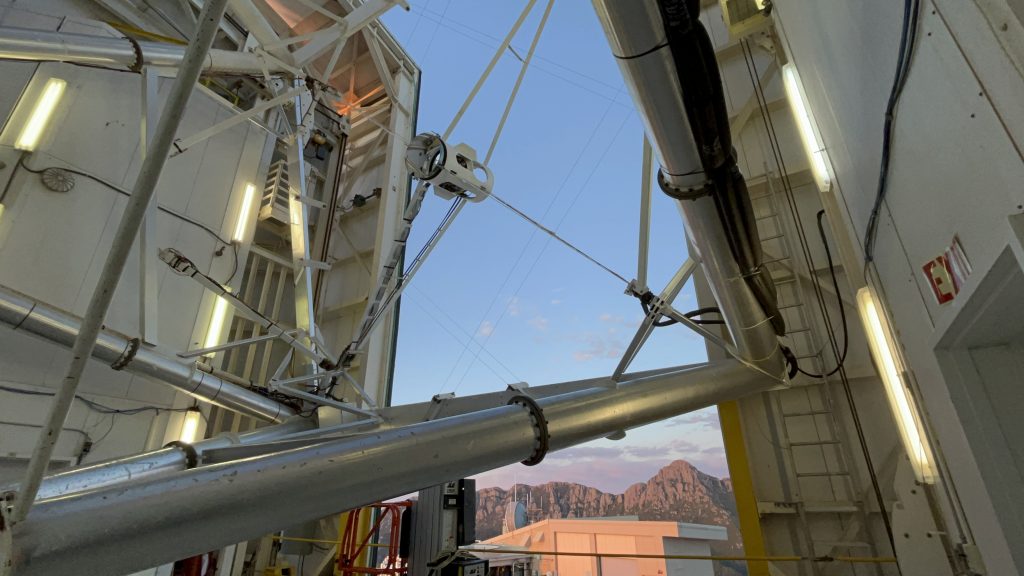

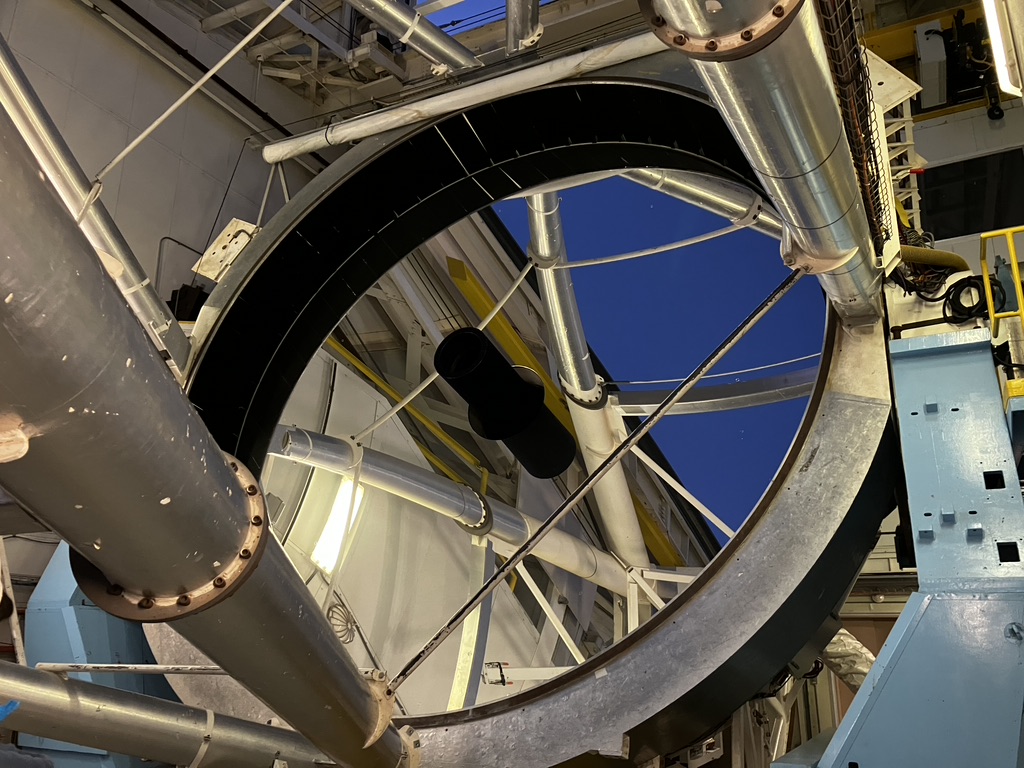
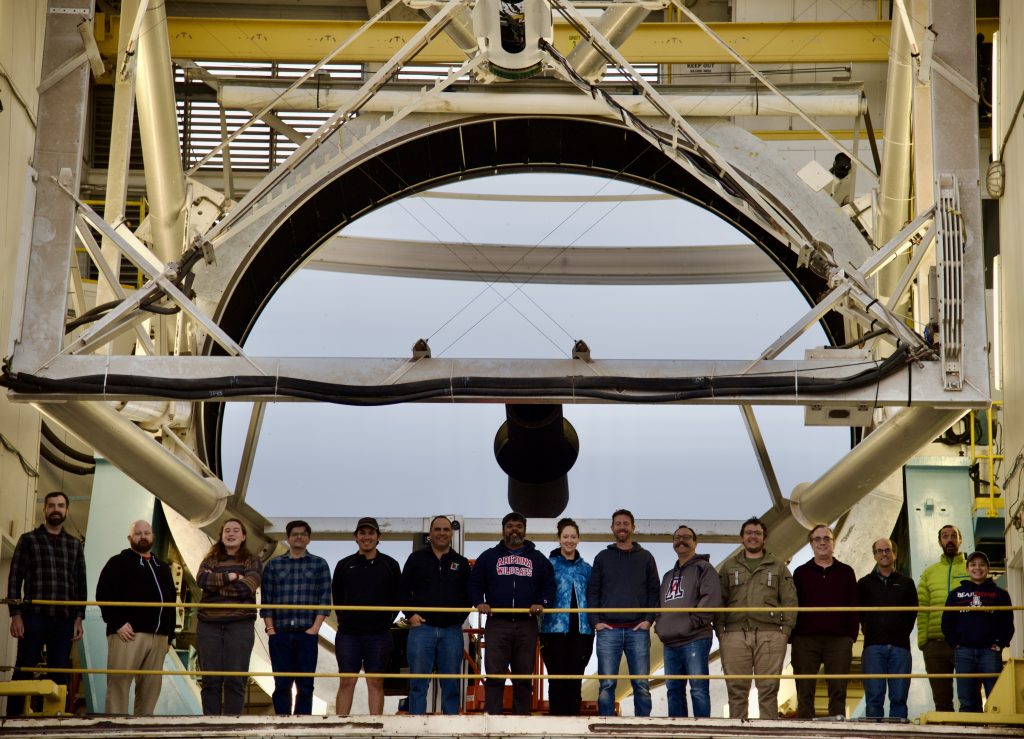
The telescope operator had kindly tipped the whole contraption over to make a compelling group photo:

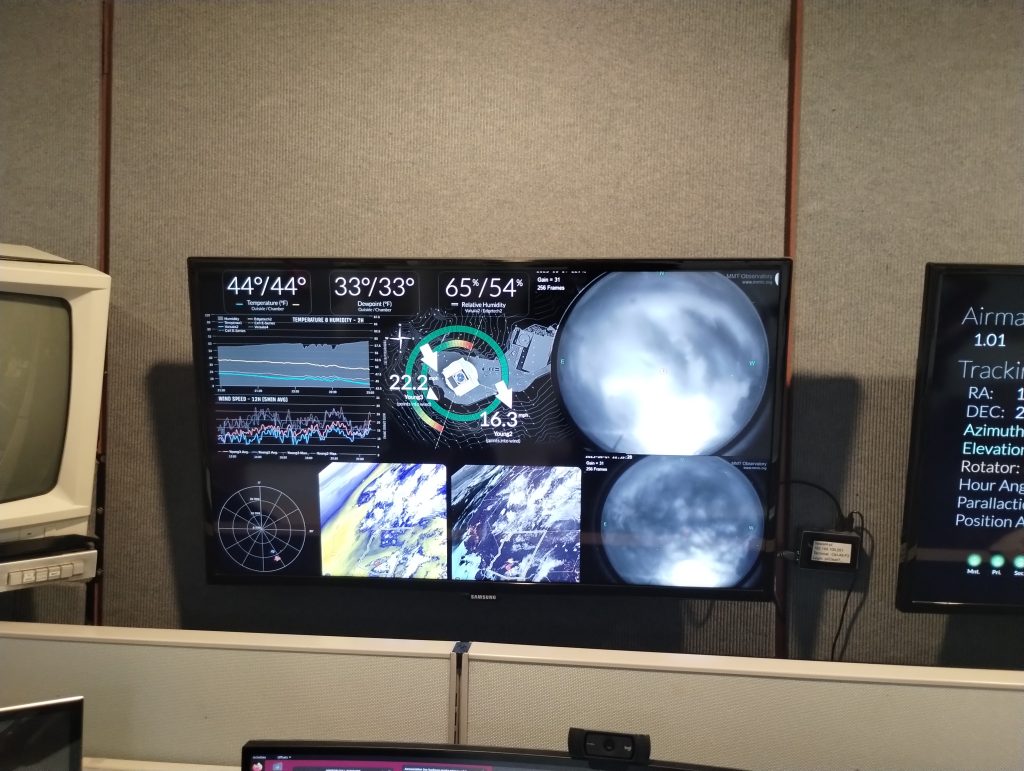
The night began with breezy but clear conditions and seeing hovering just under 1″. Naturally, the first bit of the night was spent debugging, aligning, and turning things off-and-on-again. (We know all about that.)
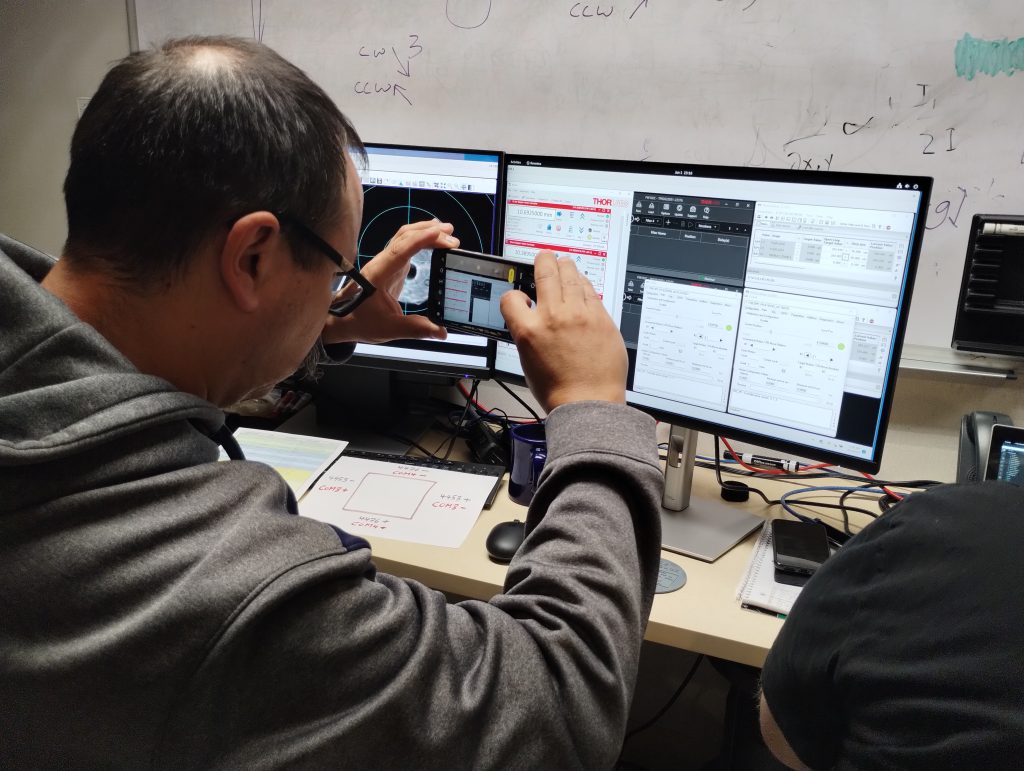
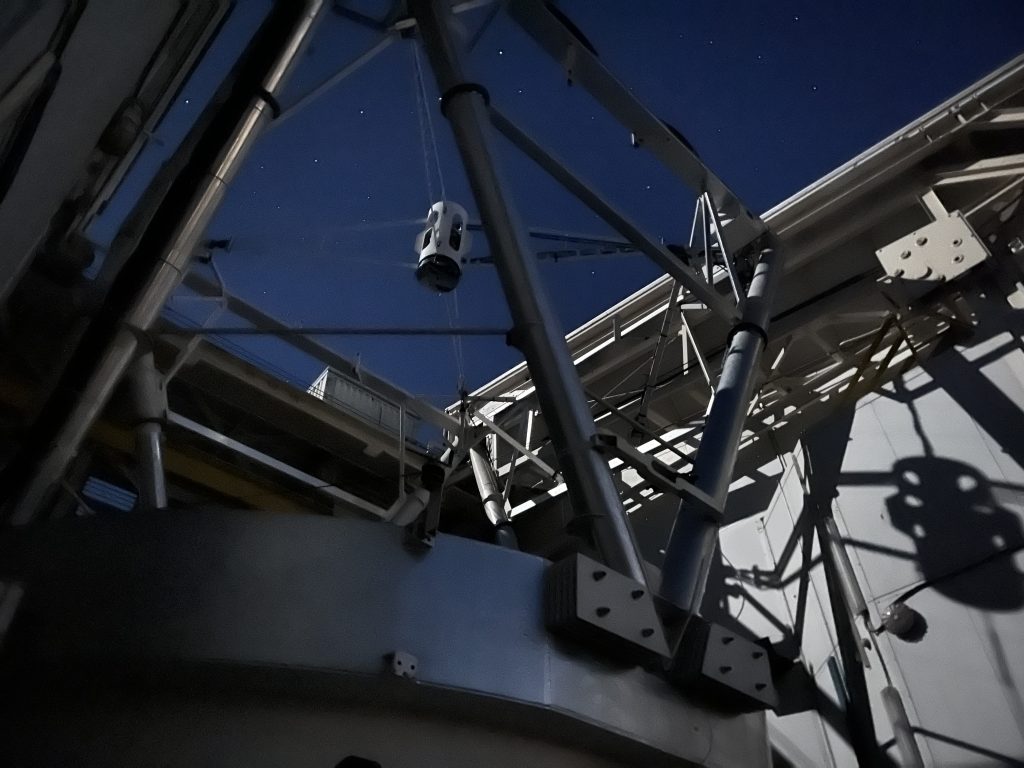
Once starlight was hitting the wavefront sensor (thanks to Oli) and the pupils were looking good and round (thanks to Robin and Jacob of UToronto): it was time for some CACAO: Compute And Control for Adaptive Optics. The same ultra-fast, ultra-flexible AO system that powers SCExAO and MagAO-X is being implemented as the new brains controlling the adaptive secondary.
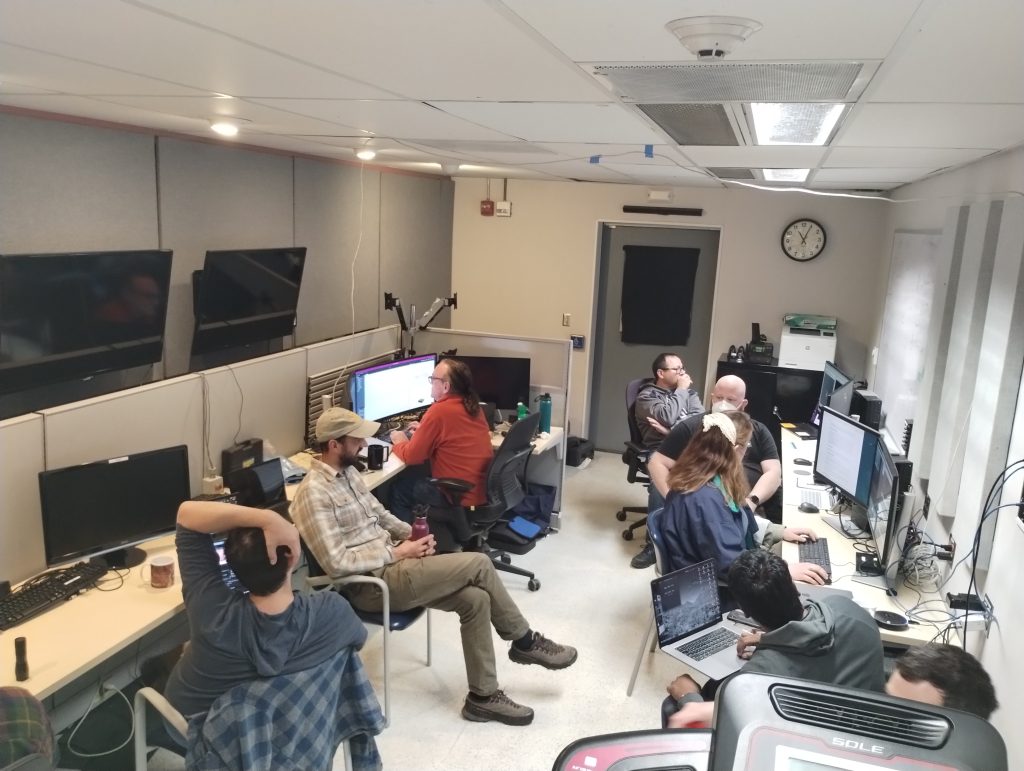
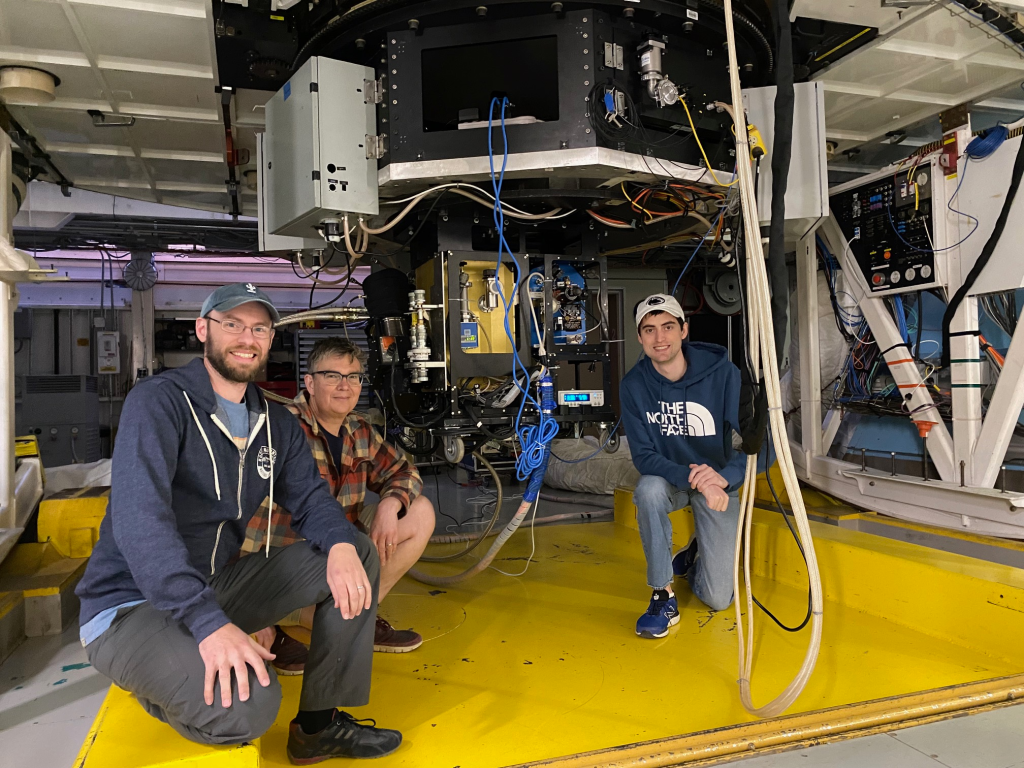
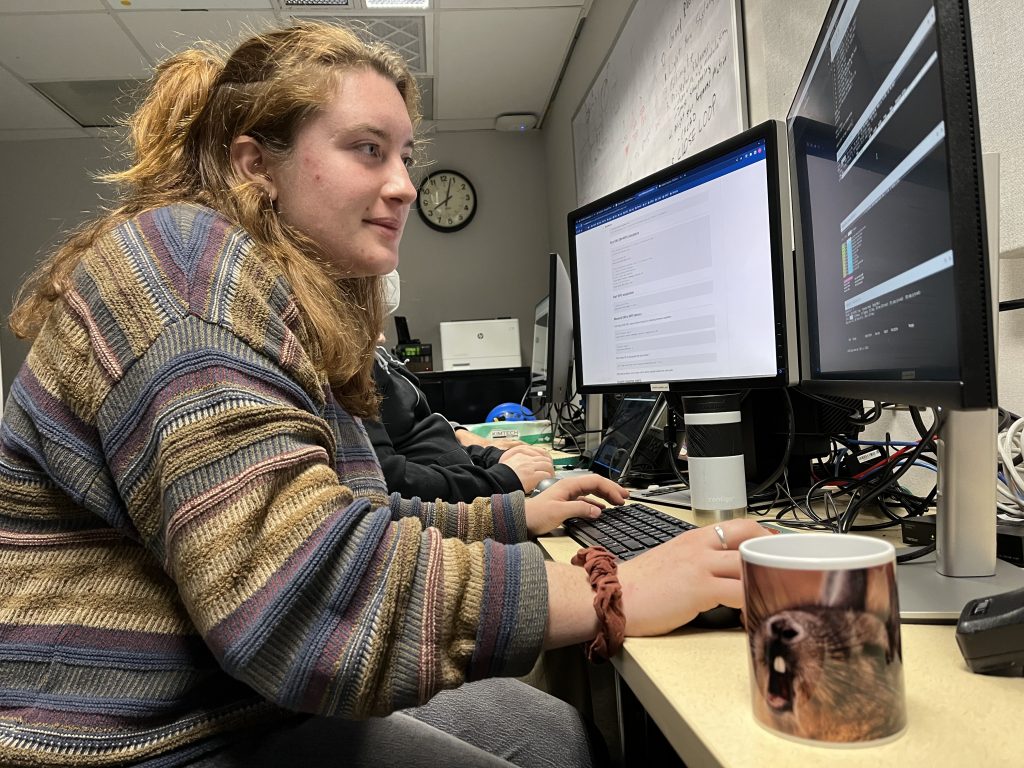
Andrew and Eden worked diligently through many fiddly bits of computer plumbing to get pixels from the sensor and commands to the adaptive secondary (under the watchful eye of Jess):

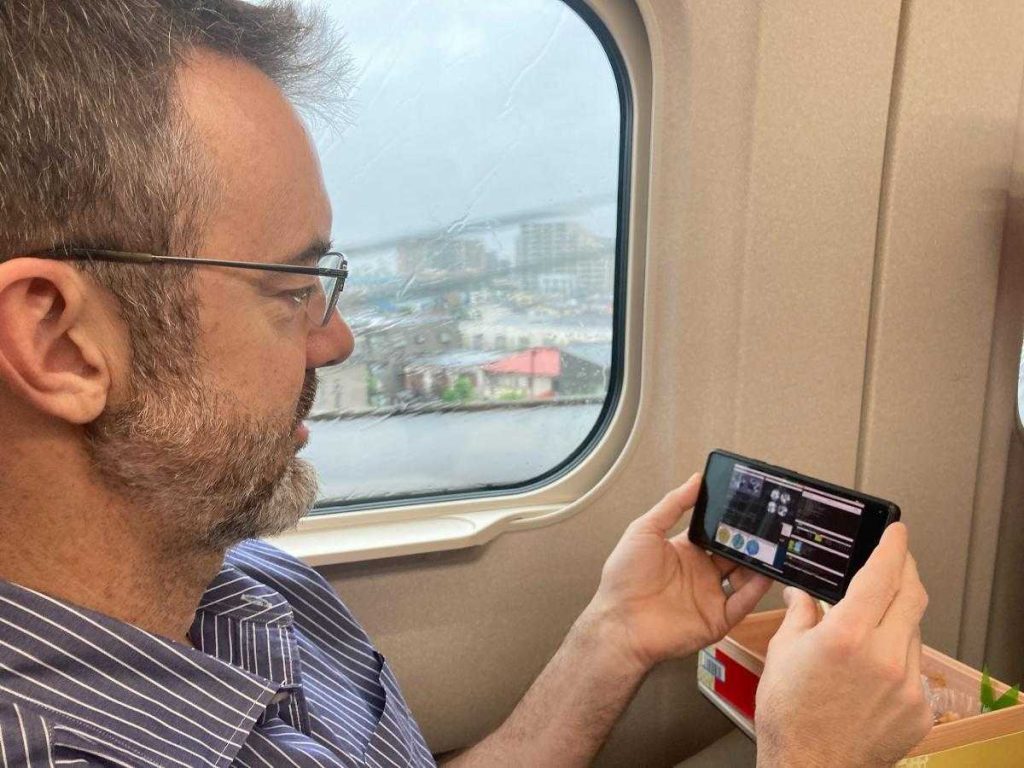
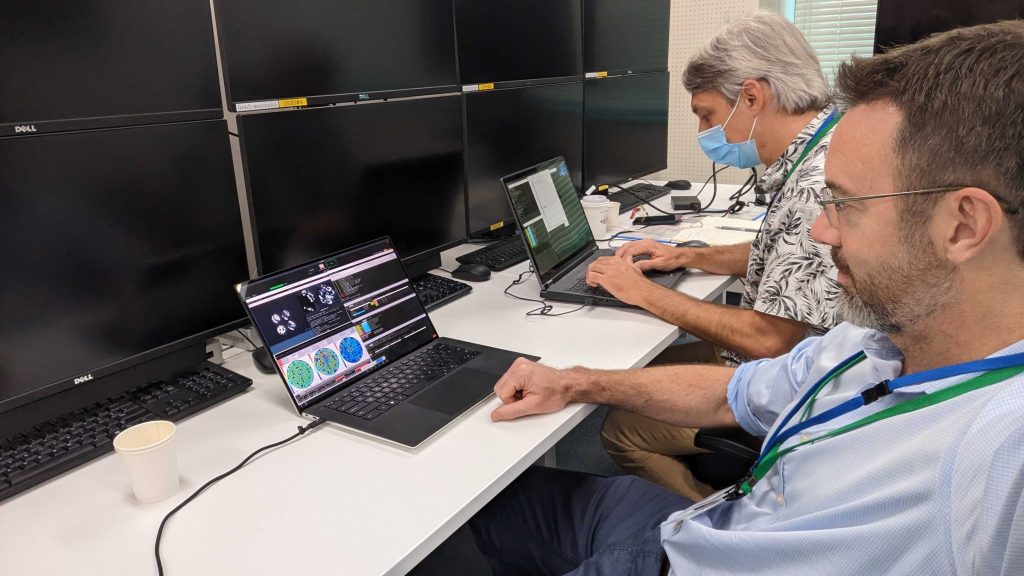
Meanwhile, in Tokyo, MAPS East was supporting the effort over Zoom:

Their combined efforts got us to our final checklist item of the night: close the loop. With an hour or so to go until sunrise, the globally distributed team worked on improving the calibration and setting things up so tomorrow night we can skip right to “the interesting part.”
Stay tuned.
Song of the Day
In honor of the MAPS East team’s contributions, I submit this Japanese groove that’s been stuck in my head.